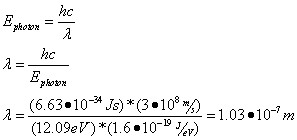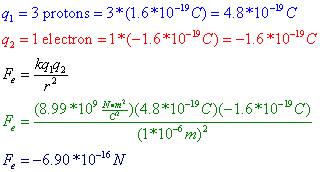
Tag Archives: atoms
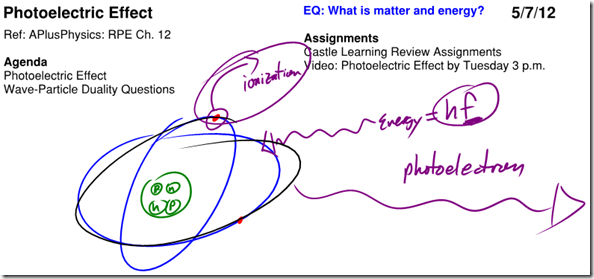
Photoelectric Effect / Models of the Atom
Models of the Atom
In the early 1900s, scientists around the world began to refine and revise our understanding of atomic structure and sub-atomic particles. Scientists understood that matter was made up of atoms, and J.J. Thompson had shown that atoms contained very small negative particles known as electrons, but beyond that, the atom remained a mystery.
Rutherford Model

New Zealand scientist Ernest Rutherford devised an experiment to better understand the rest of the atom. The experiment, known as Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment, involved shooting alpha particles (helium nuclei) at a very thin sheet of gold foil, and observing the deflection of the particles after passing through the gold foil. Rutherford found that although most of the particles went through undeflected, a significant number of alpha particles were deflected by large amounts. Using an analysis based around Coulomb’s Law and the conservation of momentum, Rutherford concluded that:
- Atoms have a small, massive, positive nucleus at the center.
- Electrons must orbit the nucleus.
- Most of the atom is made up of empty space.
Rutherford’s model was incomplete, though, in that it didn’t account for a number of effects predicted
by classical physics. Classical physics predicted that if the electron orbits the atom, it is constantly accelerating, and should therefore emit photons of EM radiation. Because the atom emits photons, it should be losing energy, therefore the orbit of the electron would quickly decay into the nucleus and the atom would be unstable. Further, elements were found to emit and absorb EM radiation only at specific frequencies, which did not correlate to Rutherford’s theory.
Bohr Model

Following Rutherford’s discovery, Danish physicist Niels Bohr traveled to England to join Rutherford’s research group and refine Rutherford’s model of the atom. Instead of focusing on all atoms, Bohr confined his research to developing a model of the simple hydrogen atom. Bohr’s model made the following assumptions:
- Electrons don’t lose energy as they accelerate around the nucleus. Instead, energy is quantized… electrons can only exist at specific discrete energy levels.
- Each atom allows only a limited number of specific orbits at each energy level.
- To change energy levels, an electron must absorb or emit a photon of energy exactly equal to the difference between the electron’s initial and final energy levels:
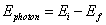
Question: Calculate the energy of the emitted photon when an electron moves from an energy level of -1.51 eV to -13.6 eV.
Answer:
Question: What is the emitted photon’s wavelength?
Answer:
Bohr’s Model, therefore, was able to explain the first two limitations of Rutherford’s Model. Further, Bohr was able to use his model to predict the frequencies of photons emitted and absorbed by hydrogen, explaining Rutherford’s problem of emission and absorption spectra! For his work, Bohr was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922.
"If quantum mechanics hasn’t profoundly shocked you, you haven’t understood it yet." — Niels Bohr
Introduction to Electrostatics
Building Blocks of Matter
Matter is made up of atoms. Once thought to be the smallest building blocks of matter, we now know that atoms can be broken up into even smaller pieces, known as protons, electrons, and neutrons. Each atom consists of a dense core of positively charged protons and uncharged (neutral) neutrons. This core is known as the nucleus. It is surrounded by a “cloud” of much smaller, negatively charged electrons. These electrons orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels. To move to a higher energy level, an electron must absorb energy. When an electron falls to a lower energy level, it gives off energy.
Most atoms are neutral — that is, they have an equal number of positive and negative charges, giving a net charge of 0. For this to occur, the number of protons must equal the number of electrons. In certain situations, however, an atom may gain or lose electrons. In these cases, the atom as a whole is no longer neutral, and we call it an ion. If an atom loses one or more electrons, it has a net positive charge, and is known as a positive ion. If, instead, an atom gains one or more electrons, it has a net negative charge, and is therefore called a negative ion. Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract each other. In physics, we represent the charge on an object with the symbol q.
Charge is a fundamental measurement in physics, much as length, time, and mass are fundamental measurements. The fundamental unit of charge is the Coulomb [C], which is a very large amount of charge. Compare that to the magnitude of charge on a single proton or electron, known as an elementary charge, which is equal to 1.6*10^-19 coulomb. It would take 6.25*10^18 elementary charges to make up a single coulomb of charge! (Don’t worry about memorizing these values, they’re listed for you on the front of the reference table!).
Question: An object possessing an excess of 6.0*10^6 electrons has what net charge?
Answer:
Conductors and Insulators
Certain materials allow electric charges to move freely. These are called conductors. Examples of good conductors include metals such as gold, copper, silver, and aluminum. In contrast, materials in which electric charges cannot move freely are known as insulators. Good insulators include materials such as glass, plastic, and rubber.
Conductors and insulators are characterized by their resistivity, or ability to resist movement of charge. Materials with high resistivities are good insulators. Materials with low resistivities are good conductors.
Semiconductors are materials which, in pure form, are good insulators. However, by adding small amounts of impurities known as dopants, their resistivities can be lowered significantly until they become good conductors.
Charging by Conduction
Materials can be charged by contact, or conduction. If you take a balloon and rub it against your hair, some of the electrons from the atoms in your hair are transferred to the balloon. The balloon now has extra electrons, and therefore has a net negative charge. Your hair has a deficiency of electrons, therefore it now has a net positive charge.
Much like momentum and energy, charge is also conserved. Continuing our hair and balloon example, the magnitude of the net positive charge on your hair is equal to the magnitude of the net negative charge on the balloon. The total charge of the hair/balloon system remains zero (neutral). For every extra electron (negative charge) on the balloon, there is a corresponding missing electron (positive charge) in your hair. This known as the law of conservation of charge.
Conductors can also be charged by contact. If a charged conductor is brought into conduct with an identical neutral conductor, the net charge will be shared across the two conductors.
Question: If a conductor carrying a net charge of 8 elementary charges is brought into contact with an identical conductor with no net charge, what will be the charge on each conductor after they are separated?
Answer: Each conductor will have a charge of 4 elementary charges.
Question: What is the net charge (in coulombs) on each conductor after they are separated?
Answer:
Coulomb’s Law
We know that like charges repel, and opposite charges attract. In order for charges to repel or attract, they apply a force upon each either. Similar to the manner in which the force of attraction between two masses is determined by the amount of mass and the distance between the masses, as described by Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation, the force of attraction or repulsion is determined by the amount of charge and the distance between the charges. The magnitude of the electrostatic force is described by Coulomb’s Law.
Coulomb’s Law states that the magnitude of the electrostatic force (Fe) between two objects is equal to a constant, k, multiplied by each of the two charges, q1 and q2, and divided by the square of the distance between the charges (r2). The constant k is known as the electrostatic constant, and is given on the reference table as: ![]() .
.
![]()
Notice how similar this formula is to the formula for the gravitational force! Both Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation and Coulomb’s Law follow the inverse-square relationship, a pattern that repeats many times over in physics. The further you get from the charges, the weaker the electrostatic force. If you were to double the distance from a charge, you would quarter the electrostatic force on a charge.

Formally, a positive value for the electrostatic force indicates that the force is a repelling force, while a negative value for the electrostatic force indicates that the force is an attractive force. Because force is a vector, you must assign a direction to it. To determine the direction of the force vector, once you have calculated its magnitude, use common sense to tell you the direction on each charged object. If the objects have opposite charges, they are being attracted, and if they have like charges, they must be repelling each other.
Question: Three protons are separated from a single electron by a distance of 1*10^-6 m. Find the electrostatic force between them. Is this force attractive or repulsive?
Answer: