Category Archives: Electricity & Magnetism
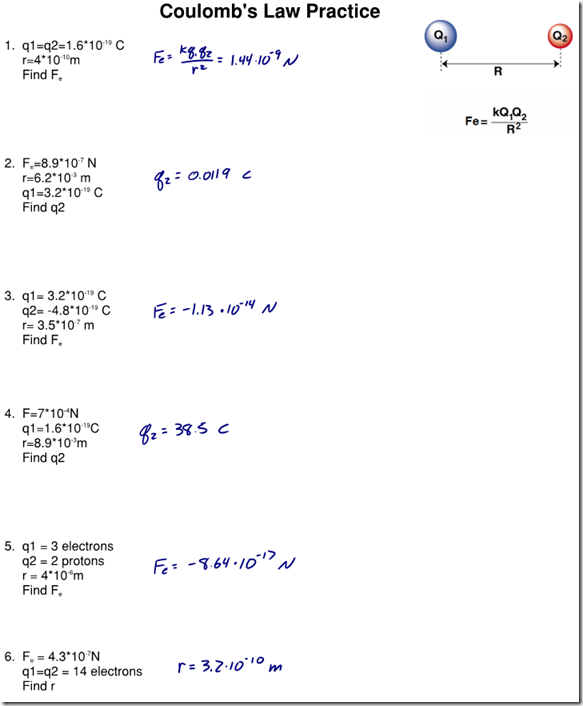
Answers to Coulomb’s Law Practice WS
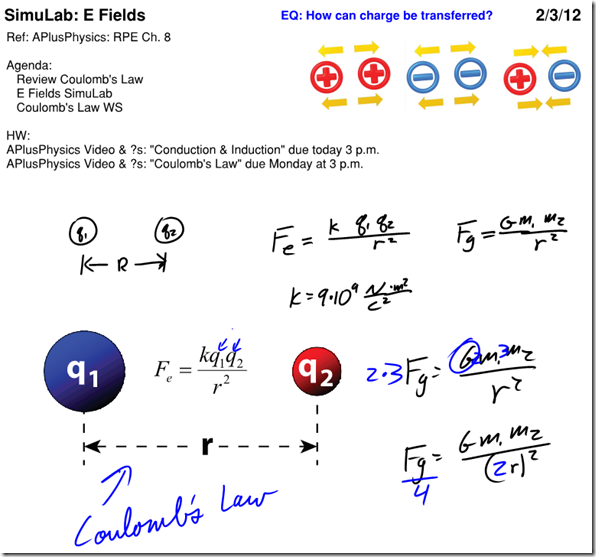
Coulomb’s Law and Electric Field SimuLAB
Electric Charges
Matter is made up of atoms. Once thought to be the smallest building blocks of matter, we now know that atoms can be broken up into even smaller pieces, known as protons, electrons, and neutrons. Each atom consists of a dense core of positively charged protons and uncharged (neutral) neutrons. This core is known as the nucleus. It is surrounded by a “cloud” of much smaller, negatively charged electrons. These electrons orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels. To move to a higher energy level, an electron must absorb energy. When an electron falls to a lower energy level, it gives off energy.
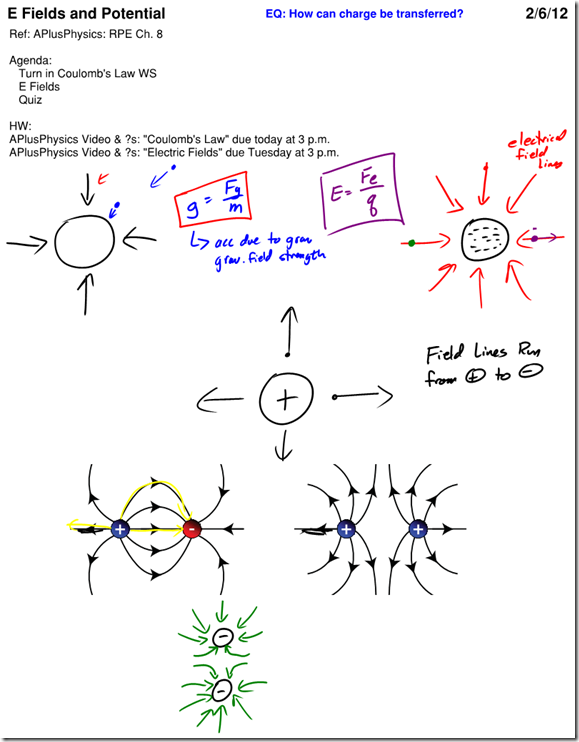
Most atoms are neutral — that is, they have an equal number of positive and negative charges, giving a net charge of 0. In certain situations, how- ever, an atom may gain or lose electrons. In these situations, the atom as a whole is no longer neutral and we call it an ion. If an atom loses one or more electrons, it has a net positive charge and is known as a positive ion. If, instead, an atom gains one or more electrons, it has a net negative charge and is therefore called a negative ion. Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract each other. In physics, we represent the charge on an object with the symbol q.
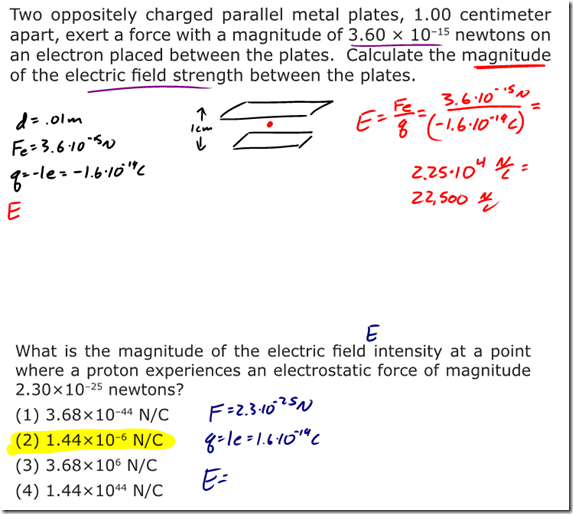
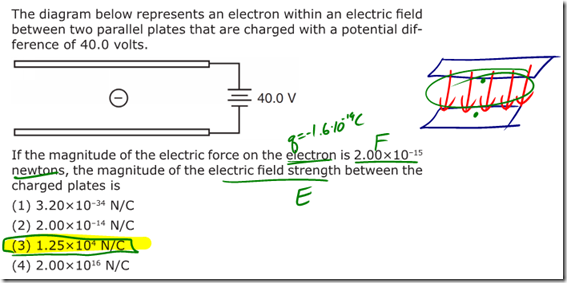
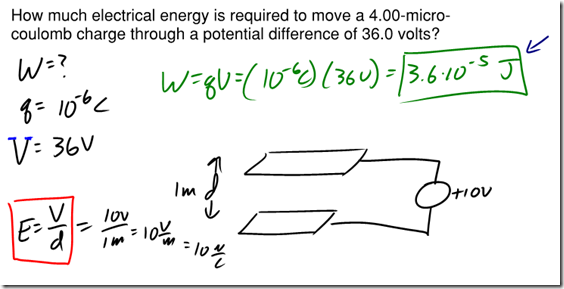
Charge is a fundamental measurement in physics, much as length, time, and mass are fundamental measurements. The fundamental unit of charge is the Coulomb [C], which is a very large amount of charge. Compare that to the magnitude of charge on a single proton or electron, known as an elemen- tary charge, which is equal to 1.6×10-19 coulomb. It would take 6.25×1018 elementary charges to make up a single coulomb of charge! (Don’t worry about memorizing these values, they’re listed for you on the front of the reference table).
Conductors and Insulators
Certain materials allow electric charges to move freely. These are called conductors. Examples of good conductors include metals such as gold, copper, silver, and aluminum. In contrast, materials in which electric charges can- not move freely are known as insulators. Good insulators include materials such as glass, plastic, and rubber. Metals are better conductors of electricity compared to insulators because metals contain more free electrons.
Conductors and insulators are characterized by their resistivity, or ability to resist movement of charge. Materials with high resistivities are good insula- tors. Materials with low resistivities are good conductors.
Semiconductors are materials which, in pure form, are good insulators. However, by adding small amounts of impurities known as dopants, their resistivities can be lowered significantly until they become good conductors.
Charging by Conduction
Materials can be charged by contact, or conduction. If you take a balloon and rub it against your hair, some of the electrons from the atoms in your hair are transferred to the balloon. The balloon now has extra electrons, and therefore has a net negative charge. Your hair has a deficiency of electrons, therefore it now has a net positive charge.
Much like momentum and energy, charge is also conserved. Continuing our hair and balloon example, the magnitude of the net positive charge on your hair is equal to the magnitude of the net negative charge on the balloon. The total charge of the hair/balloon system remains zero (neutral). For ev- ery extra electron (negative charge) on the balloon, there is a correspond- ing missing electron (positive charge) in your hair. This known as the law of conservation of charge.
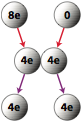
Conductors can also be charged by contact. If a charged conductor is brought into conduct with an identical neutral conductor, the net charge will be shared across the two conductors.
Question: If a conductor carrying a net charge of 8 elementary charges is brought into contact with an identical conductor with no net charge, what will be the charge on each conductor after they are separated?
Answer: Each conductor will have a charge of 4 elementary charges.
Electroscope
A simple tool used to detect small electric charges known as an electroscope functions on the basis of conduction. The electroscope consists of a conducting rod attached to two thin conducting leaves at one end and isolated from surrounding charges by an insulating stopper placed in a flask. If a charged object is placed in contact with the conducting rod, part of the charge is transferred to the rod. Because the rod and leaves form a conducting path and like charges repel each other, the charges are distributed equally along the entire rod and leaf apparatus. The leaves, having like charges, repel each other, with larger charges providing greater leaf separation!
Charging by Induction
Conductors can also be charged without coming into contact with another charged object in a process known as charging by induction. This is accomplished by placing the conductor near a charged object and grounding the conductor. To understand charging by induction, you must first realize that when an object is connected to the earth by a conducting path, known as grounding, the earth acts like an infinite source for providing or accepting excess electrons.
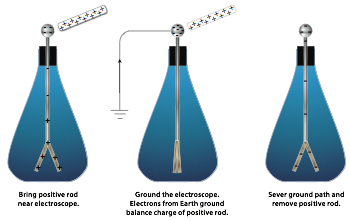
To charge a conductor by induction, you first bring it close to another charged object. When the conductor is close to the charged object, any free electrons on the conductor will move toward the charged object if the object is positively charged (since opposite charges attract) or away from the charged object if the object is negatively charged (since like charges repel).
If the conductor is then “grounded” by means of a conducting path to the earth, the excess charge is compensated for by means of electron transfer to or from earth. Then the ground connection is severed. When the originally charged object is moved far away from the conductor, the charges in the conductor redistribute, leaving a net charge on the conductor as shown.
You can also induce a charge in a charged region in a neutral object by bringing a strong positive or negative charge close to that object. In such cases, the electrons in the neutral object tend to move toward a strong positive charge, or away from a large negative charge. Though the object itself remains neutral, portions of the object are more positive or negative than other parts. In this way, you can attract a neutral object by bringing a charged object close to it, positive or negative. Put another way, a positively charged object can be attracted to both a negatively charged object and a neutral object, and a negatively charged object can be attracted to both a positively charged object and a neutral object.
For this reason, the only way to tell if an object is charged is by repulsion. A positively charge object can only be repelled by another positive charge and a negatively charged object can only be repelled by another negative charge.
Charge Sensing Lab
Regents Physics SBG Objective Tracking Sheets
10 Quick Tips to Maximize your Regents Physics Score
Although by no means an exhaustive list, these 10 quick tips may help you secure that extra point or two on your upcoming Regents Physics exam.
- Mass and inertia are the same thing.
- To find the resultant, line your vectors up tip-to-tail, and draw a line from the starting point of the first vector to the ending point of the last vector.
- Any object moving in a circular path is accelerating toward the center of the circle.
- Acceleration of an object is equal to the net force on the object divided by the object’s mass.
- The normal force always points at an angle of 90° from the surface.
- Opposite charges and magnetic poles attract, likes repel.
- Gravitational forces and electrostatic forces both follow an inverse square law relationship, where the strength of the force is related to one divided by the square of the distance between the charges/masses.
- The force of gravity on an object, commonly referred to as weight, is equal to mg, where g is the gravitational field strength (also referred to as the acceleration due to gravity).
- The mass-energy equivalence can be calculated using E=mc^2. If a mass is given in universal mass units, however, you can do a straight unit conversion using 1u = 931 MeV.
- Protons and neutrons fall into the category of baryons, which are hadrons. Smaller particles, such as electrons, fall into the category of leptons. Mesons are rare, weird particles you probably haven’t heard of.
Most importantly, use your reference table. When in doubt, write down the information you’re asked to find, what you’re given, and use your reference table to help you narrow down what you should be doing. In the free response part of the test, make sure to show your work in detail with a formula, substitution with units, and an answer with units.
Find these and many more tips for success at APlusPhysics.com.