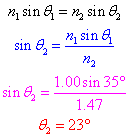When a wave reaches the boundary between media, part of the wave is reflected and part of the wave enters the new medium. As the wave enters the new medium, the speed of the wave changes, and the frequency of a wave remains constant, therefore, consistent with the wave equation, 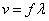 , the wavelength of the wave must change.
, the wavelength of the wave must change.
Question: When a wave enters a new material, what happens to its speed, frequency, and wavelength?
Answer: Speed changes, frequency remains constant, and wavelength changes.
The front of a wave has some actual width, therefore if the wave does not impinge upon the boundary between media at a right angle, not all of the wave enters the new medium and changes speed at the same time. This causes the wave to bend as it enters a new medium in a process known as refraction.
To better illustrate this, imagine you’re in a line in a marching band, connected with your bandmates as you march at a constant speed down the field in imitation of a wave front. As your wavefront reaches a new medium that slows you down, such as a mud pit, the band members reaching the mud pit slow down before those who reach the pit later. Since you are all connected in a wave front, the entire wave shifts directions (refracts) as it passes through the boundary between field and mud!
The index of refraction (n) is a measure of how much light slows down in a material. In a vacuum, all electromagnetic waves have a speed of c=3*108 m/s. In other materials, light slows down. The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the new material is known as the index of refraction (n). The slower the wave moves in the material, the larger the index of refraction: 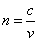
Question: A light ray traveling in air enters a second medium and its speed slows to 1.71 x 108 m/s. What is the absolute index of refraction of the second medium?
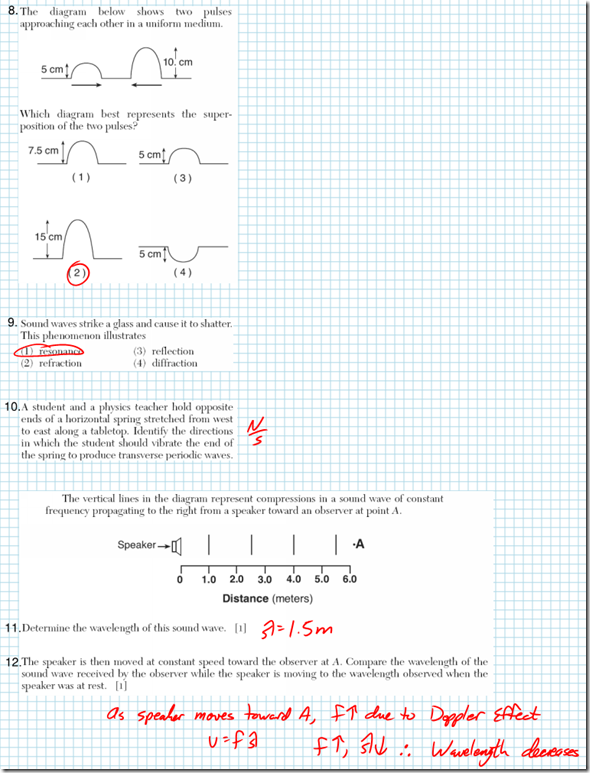
Answer: 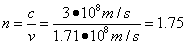

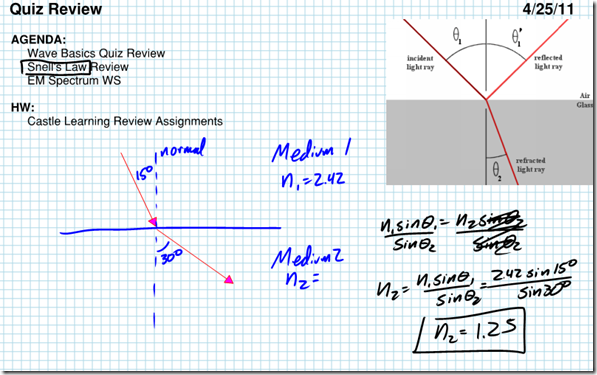
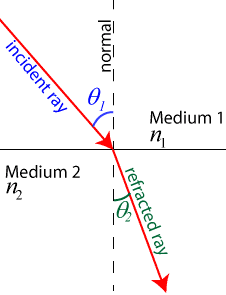
The amount a light wave bends as it enters a new medium is given by the law of refraction, also known as Snell’s Law. Snell’s Law states that 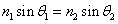 , where n1 and n2 are the indices of refraction of the media, and
, where n1 and n2 are the indices of refraction of the media, and 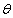 corresponds to the angles of the incident and refracted rays, again measured from the normal. Light bends toward the normal as it enters a material with a higher index of refraction (slower material), and bends away from the normal as it enters a material with a lower index of refraction (slower material).
corresponds to the angles of the incident and refracted rays, again measured from the normal. Light bends toward the normal as it enters a material with a higher index of refraction (slower material), and bends away from the normal as it enters a material with a lower index of refraction (slower material).
Not only does index of refraction depend upon the medium the light wave is traveling through, it also varies with frequency. Thankfully, its variation is typically fairly small, and the Regents Physics Reference Table even provides you a table of indices of refraction for common materials at a set frequency.
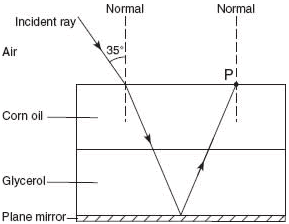
Question: A ray of monochromatic light having a frequency of 5.09 × 1014 hertz is incident on an interface of air and corn oil at an angle of 35° as shown. The ray is transmitted through parallel layers of corn oil and glycerol and is then reflected from the surface of a plane mirror, located below and parallel to the glycerol layer. The ray then emerges from the corn oil back into the air at point P.
Calculate the angle of refraction of the light ray as it enters the corn oil from air.
Answer: 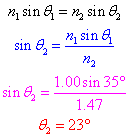
Question: Explain why the ray does not bend at the corn oil-glycerol interface.
Answer: The indices of refraction are the same for corn oil and glycerol (the speed of the wave does not change at the corn-oil / glycerol interface).