Video HW: Types of Energy
We’ve all had days where we’ve had varying amounts of energy. You’ve gotten up in the morning, had to drag yourself out of bed, force yourself to get ready to school, and once you finally get to class, you don’t have the energy to do much work. Other days, when you’ve had more energy, you may have woken up before the alarm clock, hustled to get ready for the day while a bunch of thoughts jump around in your head, and hurried on to begin your activities. Then, throughout the day, the more work you do, the more energy you lose… What’s the difference in these days?
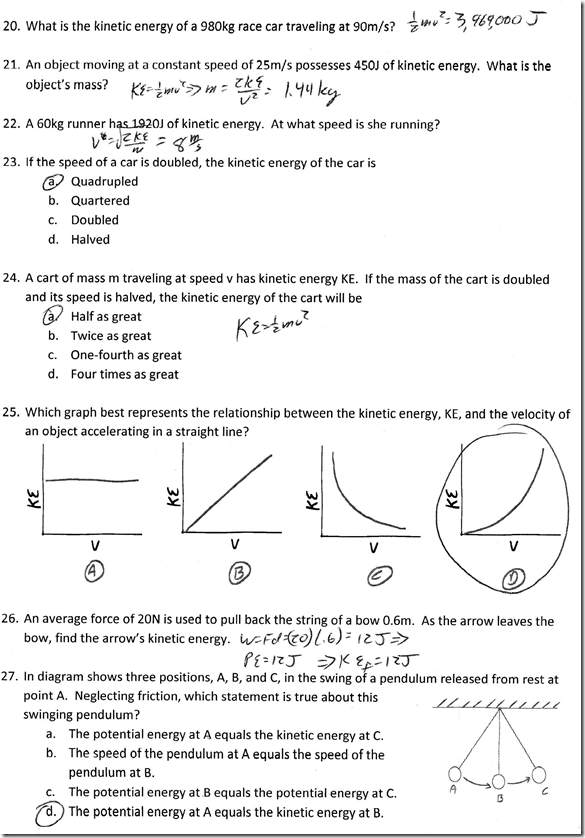
In physics, energy is the ability or capacity to do work. And as we’ve mentioned previously, work is the process of moving an object. So, if we combine our definitions, energy is the ability or capacity to move an object. And so far this year we’ve been studying kinetic energy, or energy of motion. So… kinetic energy must be the ability or capacity of a moving object to move another object!
Mathematically, kinetic energy is calculated using the formula:
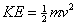
Units of energy are the same as units of work, the joule (J). By dimensional analysis, we can observe that the units of KE (kg*m2/s2) must be equal to the units of work (N*m):
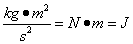
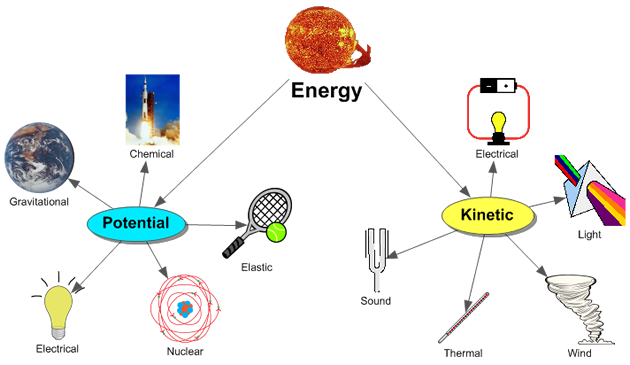
Of course, there are more types of energy than just kinetic. Energy comes in a tremendous variety of forms, which we can classify as kinetic (energy of motion) or potential (stored) to various degrees: solar energy, thermal energy, gravitational potential energy, nuclear energy, chemical potential energy, sound energy, electrical energy, elastic potential energy, light energy, and so on. In all cases, energy can be transformed from one type to another, and you can transfer energy from one object to another by doing work.
Gravitational Potential Energy
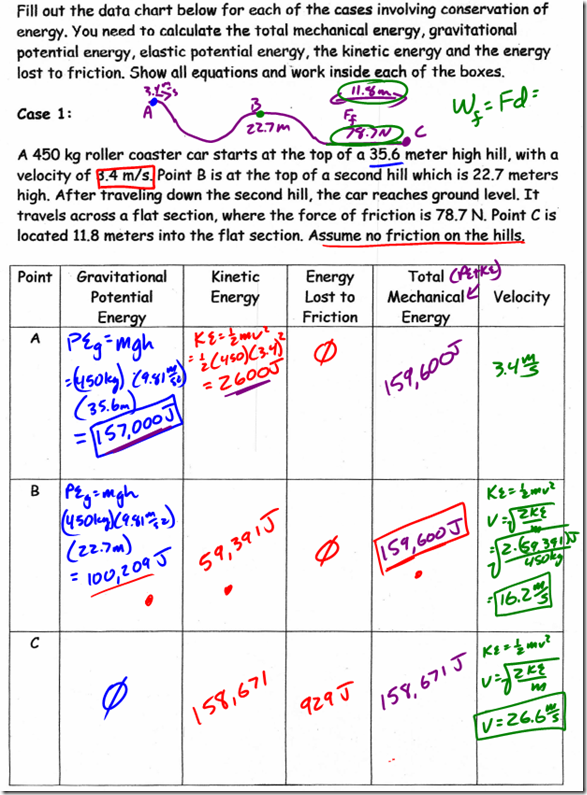
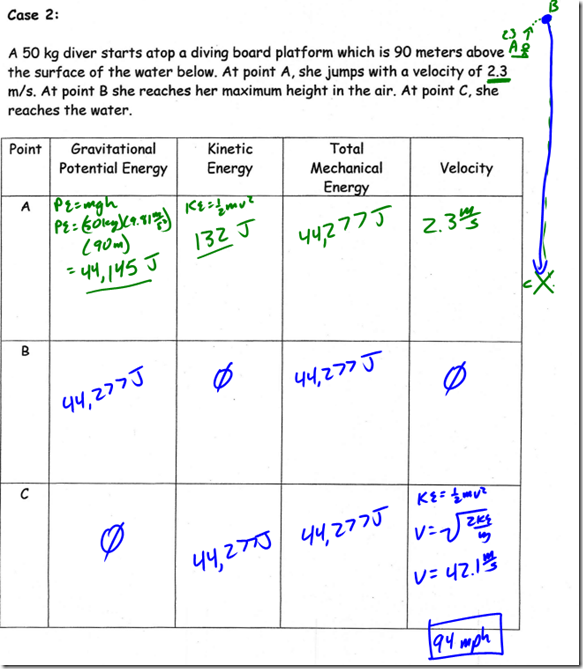
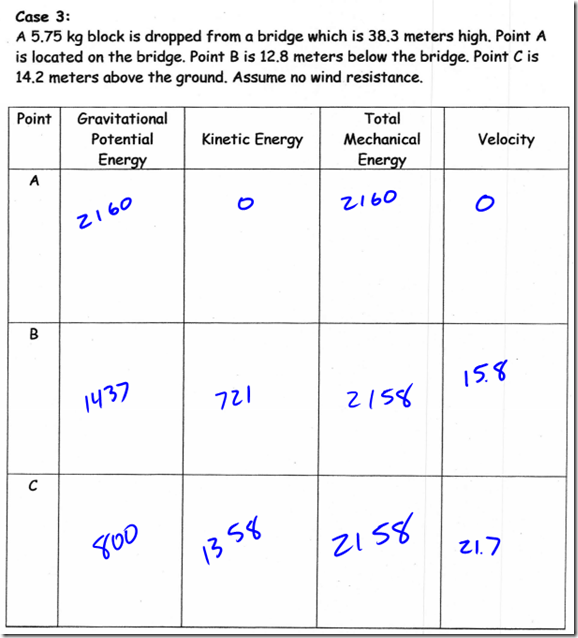
Potential energy is energy an object possesses due to its position or condition. Gravitational potential energy, then, is the energy an object possesses because of its position in a gravitational field (height).

Let’s assume we have a 10 kg box on the floor. Let’s arbitrarily call its current potential energy zero, just to give us a reference point. If we do work to lift the box one meter off the floor, we need to overcome the force of gravity on the box (its weight) over a distance of one meter. Therefore, the work we do on the box can be obtained from:
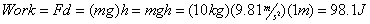
So, to raise the box to a height of 1m, the must do 98.1 Joules of work on the box. The work done in lifting the box is equal to the change in potential energy of the box, so the box’s gravitational potential energy must be 98.1J.
When we performed work on the box, we transferred some of our stored energy to the box. Along the way, it just so happens that we derived the formula for the gravitational potential energy of an object. The change in the object’s potential energy, 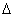 PE, is equal to the force of gravity on the box multiplied by its change in height, mg
PE, is equal to the force of gravity on the box multiplied by its change in height, mg h. This formula can be found on the reference table:
h. This formula can be found on the reference table:
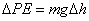
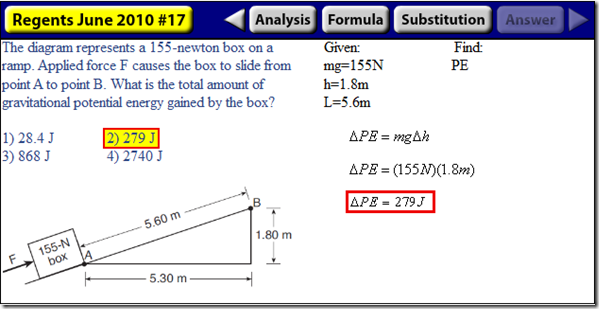
We can use this formula to solve a variety of problems involving the potential energy of an object:
Work-Energy Theorem
Of course, there are many, many different kinds of energy which we haven’t mentioned specifically. And energy can be converted among its many different forms, such as mechanical (which is kinetic, gravitational potential, and elastic potential), electromagnetic, nuclear, and thermal (or internal) energy.
When a force does work on a system, the work done changes the system’s energy. If the work done increases motion, there is an increase in the system’s kinetic energy. If the work done increases the object’s height, there is an increase in the system’s gravitational potential energy. If the work done compresses a spring, there is an increase in the system’s elastic potential energy. If the work is done against friction, however, where does the energy go? In this case, the energy isn’t lost, but instead increases the rate at which molecules in the object vibrate, increasing the object’s temperature, or internal energy.
The understanding that the work done on a system by an external force changes the energy of the system is known as the Work-Energy Theorem. If an external force does positive work on the system, the system’s total energy increases. If, instead, the system does work, the system’s total energy decreases. Put another way, you add energy to a system by doing work on it, and take energy from a system when the system does the work (much like you add value to your bank account by making a deposit, and take value from your account by writing a check).
This relationship is documented on the Regents Physics Reference Table by showing the formula for work as equal to the force times the displacement (F*d), as well as the change in total energy ( E):
E): 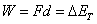 .
.
Sources of Energy on Earth

So where does all this energy initially come from? Here on Earth, the energy we deal with everyday ultimately comes from the sun. The sun’s radiation provides an energy source for life on earth, which over the millenia has become the source of our fossil fuels. The sun’s radiation also provides the thermal and light energy that heat the atmosphere and cause the winds to blow. The sun’s energy evaporates water, which eventually recondenses as rain and snow, falling to the Earth’s surface to create lakes and rivers, with gravitational potential energy, which we may harness in hydroelectric power plants. Just try to find an energy source on the Earth that doesn’t originate with the sun!