Electricity in the Brain
More electricity-themed blog posts! ![]()
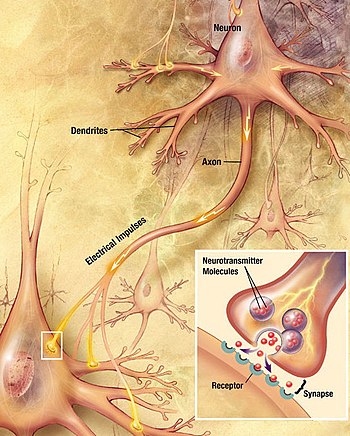
Neurons are cells in the nervous system. This cell transfers information via chemical and electrical signals. The long, stem-like part of a nerve cell is called the axon. In the human body, the axons that run from your spinal chord to your feet can be over a meter long. Electrical pulses are transferred through the axon down to the neurotransmitter molecules. The membrane potential of the average neuron cell is between -60 and -80 mV when the cell is not transmitting signals.

The electrical signal is converted into a chemical one once it reaches the synapse. The synaptic vesicles (containing ligands called neurotransmitters) release small molecules, which flow over to the receptor molecules on the adjacent nerve cell, and the message travels through a net of these cells until it reaches its destination.
Some interesting facts about the nervous systems of various species:
-- The electric eel is equip with 8,400 neurons, which can potentially crank out a painful 600 V.
-- It is estimated that the human brain contains roughly 100 billion nerve cells.
-- All animals except sponges have a type of nervous system.
-- The contraction and expansion of a Hydra is controlled by a nerve net, a web-like system of neurons that span the organism's body.
Shocking, eh? :einstein)
--Alpha Geek



0 Comments
Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.