Considering an AP Physics course? Outstanding, but which course should you take? The College Board now offers four separate and distinct versions of AP Physics, each designed with very different content, styles, and levels of mathematical complexity.
Currently, the four physics courses offered are AP Physics 1, AP Physics 2, AP Physics C: Mechanics, and AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism. So let’s start by talking about the courses and what each has to offer.
Algebra-Based Courses
The new AP Physics 1 and 2 courses are both algebra-based courses, meaning no knowledge of calculus is required, though students should be comfortable with basic algebra and trigonometry. The exams for these courses were first offered in May of 2015, so the courses and the exams are still evolving through their infancy. Further, the AP Physics 1 and AP Physics 2 courses include a strong emphasis on conceptual understanding and critical thinking. Compared to traditional physics courses, these courses include a significant amount of reading and structured writing, experimental design, and critical thinking.
Though mathematical reasoning and problem-solving are required for success in the course, they aren’t emphasized as strongly as in traditional courses. The courses are centered around seven “big ideas in physics,” and many of the exam problems will test your ability to interpret and apply one or more of these ideas to a new and unique situation (sometimes referred to as a transfer task).
Like most introductory physics courses, both AP Physics 1 and AP Physics 2 include a strong lab component to help students develop proficiency in science practices which are crucial to success. The course as a whole focuses on the idea that physics is something you do, not just something you know.
The associated AP exams for these courses consist of two sections: a 90-minute multiple choice section and a 90-minute free response section. The multiple choice section consists of 50 to 55 questions with four answer choices per question. Unlike most multiple choice tests, however, certain questions may have multiple correct answers that need to be chosen to receive full credit.
The free response section consists of four or five questions. Typically one question will cover experimental design, one question will cover quantitative and qualitative problem solving and reasoning, and three questions are of the short answer variety. In addition, students are expected to articulate their answers with a paragraph-length response.
AP Physics 1
The AP Physics 1 course itself is designed as a first-year physics course. The bulk of the course centers around traditional Newtonian Mechanics, beginning with the study of motion (kinematics), forces (dynamics), work, energy, power, linear momentum, circular motion and rotation, gravity, and oscillations. In addition, AP Physics 1 also includes a brief introduction to mechanical waves, basic electrostatics, and simple electrical circuits.
AP Physics 2
AP Physics 2 is designed as a follow-up to AP Physics 1, utilizing the same course philosophy, but extending the content covered to include fluids, thermal physics, a deeper look at electrostatics and more complex electrical circuits, magnetism, optics, and modern physics.
Calculus-Based Courses
The two AP Physics C courses both incorporate calculus, so students should have calculus as a pre-requisite or co-requisite for the best possible experience. AP Physics C: Mechanics can be offered as a first-year physics course, though some schools offer both AP Physics C: Mechanics and AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism in the same year to students who have prior physics courses in their background.
Compared to AP Physics 1 and AP Physics 2, the AP Physics C courses follow a more traditional path with a stronger emphasis on quantitative problem solving. The level of calculus complexity is relatively light, with a strong focus on application of principles to various situations as opposed to the longer written explanations of the AP–1 and AP–2 courses.
AP Physics C: Mechanics
Similar to AP Physics 1, AP Physics C: Mechanics covers only traditional Newtonian Mechanics. Students study motion, forces, work, energy, power, linear momentum, angular momentum, circular motion, rotational motion, gravity, and oscillations. Compared to AP Physics 1, however, the C course incorporates a higher level of technical complexity, such as dealing with situations of a non-constant acceleration, incorporation of drag forces (such as air resistance), and calculations of rotational inertia.
Both of the AP-C exams consist of roughly 35 multiple choice questions given in a 45-minute interval, followed by three free response questions in a second 45-minute interval. The AP-C exams are typically given back to back on the same afternoon.
AP Physics C: Electricity & Magnetism
The AP Physics C: Electricity & Magnetism course is by far the most technically complex of the AP Physics courses. Beginning with electrostatics, the course includes a detailed look at charges, electric forces, electric fields, electric potential, and capacitors. These concepts are then applied to an analysis of electrical circuits, including circuits with multiple sources of potential difference, real and ideal batteries, and transient analyses of circuits which include capacitors.
From there, the course transitions into a look at magnetism, with a strong focus on the relationships between electricity and magnetism as Maxwell’s Equations are investigated. It’s typically in this section that students really begin to challenge themselves, applying fundamental relationships (and calculus skills) to problems of increasing sophistication and technical complexity. With the added knowledge of magnetism, inductors are also discussed and tied back into the analysis of electrical circuits.
As you can see from the course descriptions, both of the AP Physics C courses are quite limited in scope, allowing for a much deeper exploration of the fundamental relationships and their application to various problems and situations.
Long-Term Goals
So then, back to our original question – which AP Physics course should you take? The answer, as is so often the case in life, is that it depends. Students who are planning on a career in engineering or physics should definitely consider the calculus-based courses (AP Physics C). These courses are fundamental to future studies, and a majority of colleges and universities accept scores of 4 or 5 in these courses for credit (though many students choose to re-take these courses to further cement their understanding of the fundamental concepts and boost their freshman GPA).
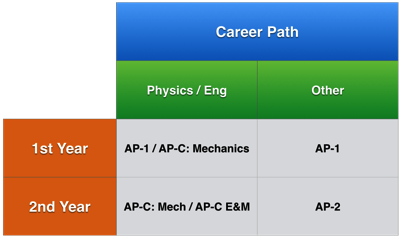
For students who aren’t planning on a career in engineering or physics, the AP Physics 1 / AP Physics 2 series might be a better answer if their school of choice accepts AP–1/2 credit, as AP Physics C could be “overkill” compared to future course requirements. The problem, however, is that the AP Physics 1 and AP Physics 2 courses are so new that many colleges don’t know how to deal with them, and as of the writing of this article, there aren’t many schools that provide college credit for strong scores on the exams, as the course content and philosophy often times don’t match up well with the college’s offerings. For this reason, students who are up for a challenge and enjoy problem solving may want to target the AP Physics C course, even if they aren’t planning on a career in engineering or physics. Many universities will give credit for a good score in AP Physics C as a general science credit.
To complicate matters, there are often times opportunities to take a sequence of these courses. In many high schools, AP Physics C is offered as a second-year physics course, with students taking on both the Mechanics and E&M courses in a single year. It’s a fast-paced course, but doable for those who have successfully passed an introductory physics course. For those taking physics for the first time, AP Physics C: Mechanics is a reasonable year-long endeavor. Some schools with extended class times offer both AP–1 and AP–2 in the same year, though this is a very aggressive undertaking.
Summarizing the Choices
To summarize as best I can in this nebulous time period, AP Physics C courses are traditionally for students heading toward physics and/or engineering related career paths, and require a pre-requisite or co-requisite in calculus. Definitely take AP-C Mechanics before AP-C E&M, though it is possible to do both in the same year, especially with some prior physics background. For students not taking calculus or not headed toward physics or engineering careers, AP Physics 1 is a great place to start, with AP Physics 2 a reasonable follow-up for those interested. The concern with these choices is the newness of the courses, and whether colleges and universities will give credit for a strong AP score. As always, discussing and planning out course selections with a guidance counselor in consultation with an admissions counselor is highly advised.
Strategies for Success
Regardless of which course(s) you choose, the AP Physics courses are challenging courses that require a level of independence and personal accountability to learn the material. These courses aren’t designed for “spoon feeding,” in which the instructor lectures, students listen, and everything works out. In order to truly understand the material and perform well on the culminating exam, you must engage in the class on a daily basis, struggle through the challenging problems, make mistakes again and again, and learn from them. Actively participate in classroom and lab activities and discussions, ask questions, but be prepared to search out your own answers. And don’t be afraid to take a step back every now and then and think about how what you’re learning applies to the course goals as a whole. Concept-mapping or outlining the topics in the course can be a terrific way to make connections you might not otherwise recognize.
And of course, you have tons of resources to help you. Beyond just your textbook (which I do recommend you actually open and actively read) and teacher, you’ll find outstanding video tutorials and Q&A forums like those at Educator.com, discussion and homework help communities, “cheat sheets,” and extra problems at APlusPhysics.com, and of course there are some great review and companion books available for these specific courses.
About the Author
Dan Fullerton is the author of AP Physics 1 Essentials, AP Physics 2 Essentials, and the APlusPhysics.com website. He is an AP Physics teacher at Irondequoit High School in Rochester, NY, and was named a New York State Master Physics Teacher in 2014.
AP and Advanced Placement Program are registered trademarks of the College Board, which does not sponsor or endorse this work.

 what does this change entail, and why has this change been undertaken? A study by the
what does this change entail, and why has this change been undertaken? A study by the 

 About the Author –
About the Author –